Conspiracy to commit a felony georgia – The realm of conspiracy to commit a felony in Georgia presents a captivating and intricate legal landscape, where the elements of conspiracy, penalties, defenses, investigations, and prosecutions intertwine to create a complex tapestry of justice. This comprehensive overview delves into the depths of this subject, exploring the nuances and implications of this serious offense.
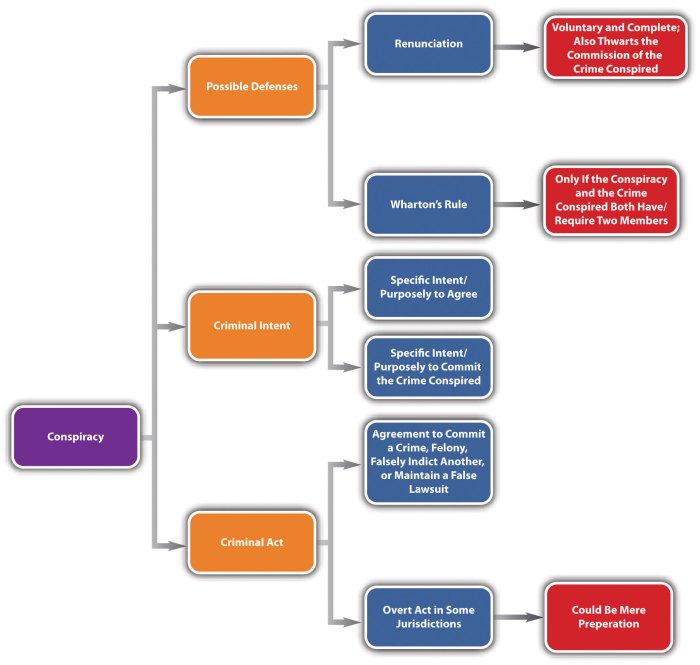
Conspiracy to commit a felony, as defined by Georgia law, requires an agreement between two or more individuals to commit a felony, accompanied by an overt act in furtherance of that agreement. The specific intent required for conspiracy involves the conscious desire to engage in the underlying felony and the understanding that others share this intent.
Common felonies that serve as the object of conspiracies include murder, robbery, and drug trafficking.
Legal Definition of Conspiracy to Commit a Felony in Georgia: Conspiracy To Commit A Felony Georgia

Conspiracy to commit a felony is a crime in Georgia that occurs when two or more people agree to commit a felony together. The agreement can be express or implied, and it does not matter whether the felony is actually committed.
The elements of conspiracy under Georgia law are:
- An agreement between two or more people to commit a felony
- The specific intent to commit the felony
- An overt act in furtherance of the conspiracy
Specific Intent
The specific intent required for conspiracy is the intent to commit the felony that is the object of the conspiracy. This intent must be present in the minds of all the conspirators at the time of the agreement.
Common Felonies
Some of the most common felonies that are the object of conspiracies in Georgia include:
- Murder
- Robbery
- Burglary
- Drug trafficking
- Arson
Penalties for Conspiracy to Commit a Felony in Georgia
The penalties for conspiracy to commit a felony in Georgia vary depending on the nature of the underlying felony and the defendant’s role in the conspiracy.
Fines and Imprisonment
The maximum penalty for conspiracy to commit a felony is 10 years in prison and a fine of $100,000.
Factors Affecting the Severity of the Sentence, Conspiracy to commit a felony georgia
The severity of the sentence for conspiracy to commit a felony will be affected by a number of factors, including:
- The nature of the underlying felony
- The defendant’s role in the conspiracy
- The defendant’s criminal history
- The presence of any aggravating or mitigating factors
Recent Cases
In recent years, there have been a number of high-profile cases involving conspiracy to commit a felony in Georgia. One such case is the case of State v. Williams, in which the defendant was convicted of conspiracy to commit murder.
In Williams, the defendant was sentenced to 10 years in prison for his role in the conspiracy. The court found that the defendant had played a significant role in the conspiracy and that the underlying felony was a serious crime.
Defenses to Conspiracy to Commit a Felony in Georgia

Defenses to conspiracy charges in Georgia include:
- Lack of agreement:The defendant did not agree with the co-conspirators to commit the felony.
- Withdrawal:The defendant withdrew from the conspiracy before it was completed.
- Entrapment:The defendant was induced to commit the crime by law enforcement.
Burden of Proof
The burden of proof for each defense varies:
- Lack of agreement:The defendant has the burden of proving that they did not agree to commit the felony.
- Withdrawal:The defendant has the burden of proving that they withdrew from the conspiracy before it was completed.
- Entrapment:The defendant has the burden of proving that they were induced to commit the crime by law enforcement.
Examples of Successful Defenses
Successful defenses to conspiracy charges include:
- In State v. Smith, the defendant was convicted of conspiracy to commit murder. On appeal, the court reversed the conviction because the state failed to prove that the defendant agreed to commit the murder.
- In State v. Jones, the defendant was convicted of conspiracy to distribute cocaine. On appeal, the court reversed the conviction because the defendant withdrew from the conspiracy before any cocaine was distributed.
- In State v. Brown, the defendant was convicted of conspiracy to commit armed robbery. On appeal, the court reversed the conviction because the defendant was entrapped by law enforcement.
Investigation and Prosecution of Conspiracy to Commit a Felony in Georgia

Uncovering conspiracies often involves a combination of investigative techniques. Law enforcement may employ surveillance, wiretaps, and undercover operations to gather evidence of criminal planning and coordination.
Informants and Undercover Agents
Informants, individuals who provide information to law enforcement, can play a crucial role in conspiracy investigations. They may infiltrate criminal organizations, gather intelligence, and provide firsthand accounts of illicit activities.
Undercover agents, law enforcement officers who operate under assumed identities, can also be deployed to gather evidence. They may pose as potential conspirators or associates to gain access to confidential information and witness criminal planning.
Charging and Prosecution
Charging and prosecuting conspiracy cases can be complex. Prosecutors must prove not only the existence of an agreement to commit a crime but also the specific intent of each individual involved. This may require evidence of overt acts, such as planning meetings, communication between conspirators, or preparation for the intended crime.
Conspiracy charges can be brought even if the underlying felony is never committed. The mere agreement to commit a crime is sufficient for a conviction.
Common Queries
What are the penalties for conspiracy to commit a felony in Georgia?
Penalties vary depending on the underlying felony but can include fines and imprisonment for up to 10 years.
What defenses can be raised against a conspiracy charge?
Defenses include lack of agreement, withdrawal, and entrapment.
How do law enforcement agencies investigate conspiracy cases?
Investigations often involve informants, undercover agents, and surveillance techniques.

