Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey with our comprehensive Period 7 APUSH Study Guide. This meticulously crafted guide delves into the pivotal events that shaped the United States, from the American Revolution to the transformative Obama Era.
Our study guide offers a captivating narrative that brings history to life, exploring the causes, consequences, and lasting impacts of each era. With clear timelines, engaging descriptions, and thought-provoking discussions, this guide will empower you to excel in your APUSH studies.
American Revolution
The American Revolution, a pivotal conflict in the late 18th century, marked a significant turning point in the history of the United States. It ignited a chain of events that led to the declaration of independence from British rule and the establishment of a new nation founded on the principles of democracy and self-governance.
For those looking to excel in their Period 7 APUSH studies, it’s essential to understand the intricacies of court cases that shaped the era. One such case is Dalal v. City of New York , which explored the complex interplay between civil rights and law enforcement.
By delving into such landmark cases, students can gain a deeper understanding of the legal and social forces that influenced American history during Period 7.
Causes of the American Revolution
The roots of the American Revolution can be traced to a complex interplay of political, economic, and social factors that strained the relationship between the British colonies in North America and the British government. Some of the key causes included:
- Political Grievances:The colonists resented the perceived lack of representation in the British Parliament, which imposed taxes and regulations without their consent. The Stamp Act of 1765 and the Townshend Acts of 1767 sparked widespread protests and ignited the flames of resistance.
- Economic Tensions:The British government’s policies, such as the Navigation Acts, restricted colonial trade and hindered economic growth. The colonists sought greater economic autonomy and control over their own affairs.
- Ideological Differences:Enlightenment ideas about natural rights, self-government, and individual liberty gained traction in the colonies. These ideas clashed with the British concept of imperial authority, setting the stage for a philosophical divide.
Timeline of Major Events
The American Revolution unfolded through a series of significant events:
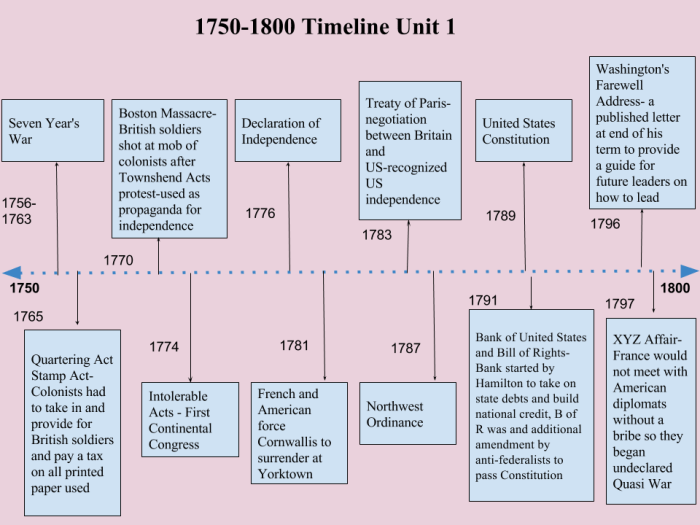
- 1774: First Continental Congress
Representatives from twelve colonies convened in Philadelphia to discuss their grievances and coordinate resistance.
- 1775: Battles of Lexington and Concord
Armed clashes between British troops and colonial militia marked the outbreak of open hostilities.
- 1776: Declaration of Independence
The Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence, formally severing ties with Great Britain.
- 1777: Battle of Saratoga
A decisive American victory that convinced France to enter the war on the side of the colonies.
- 1781: Battle of Yorktown
The combined forces of the Continental Army and French troops surrounded and defeated the British army, effectively ending the war.
Impact of the American Revolution
The American Revolution had a profound impact on the United States:
- Independence and Sovereignty:The colonies gained their independence and established the United States of America as a sovereign nation.
- Democratic Principles:The revolution laid the foundation for democratic principles and self-governance, enshrined in the Constitution and Bill of Rights.
- Expansion and Growth:The newly independent nation embarked on a period of westward expansion, acquiring new territories and increasing its economic and political power.
- Global Influence:The American Revolution became a symbol of liberty and democracy, inspiring other revolutions and movements for independence worldwide.
The Constitution
The Constitution is the supreme law of the United States. It establishes the framework for the national government and guarantees the rights of its citizens. The Constitution was drafted in 1787 and ratified in 1789.
Key Principles of the Constitution
The Constitution is based on several key principles, including:
- Popular sovereignty: The government derives its power from the consent of the governed.
- Limited government: The government is limited in its powers by the Constitution.
- Separation of powers: The government is divided into three branches (legislative, executive, and judicial) to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful.
- Checks and balances: Each branch of government has the ability to check the power of the other branches.
- Judicial review: The Supreme Court has the power to declare laws unconstitutional.
Comparison of the Articles of Confederation to the Constitution
The Articles of Confederation were the first constitution of the United States. They were adopted in 1781 and established a loose confederation of states. The Articles of Confederation were weak and ineffective, and they were replaced by the Constitution in 1789.The
Constitution differed from the Articles of Confederation in several key ways. First, the Constitution created a stronger national government. The Articles of Confederation gave most of the power to the states, while the Constitution gave more power to the federal government.
Second, the Constitution established a system of checks and balances. The Articles of Confederation did not have a system of checks and balances, which allowed the states to become too powerful. Third, the Constitution created a Supreme Court. The Articles of Confederation did not have a Supreme Court, which meant that there was no way to enforce the laws of the confederation.
Branches of Government Created by the Constitution
The Constitution created three branches of government: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.
- The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. It is composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives.
- The executive branch is responsible for enforcing laws. It is composed of the President, the Vice President, and the Cabinet.
- The judicial branch is responsible for interpreting laws. It is composed of the Supreme Court, the lower federal courts, and the state courts.
The three branches of government are coequal, and each branch has the ability to check the power of the other branches. This system of checks and balances helps to ensure that no one branch of government becomes too powerful.
Westward Expansion
Westward Expansion, a defining chapter in American history, propelled the nation’s boundaries from the Atlantic coast to the Pacific Ocean. Driven by an array of motivations, this relentless westward surge left an indelible mark on the United States.
Motivations for Westward Expansion
The allure of westward expansion stemmed from a confluence of factors:
- Economic Opportunities:Vast tracts of fertile land beckoned settlers seeking economic prosperity. The promise of homesteads, mineral wealth, and new markets fueled the westward migration.
- Political Ambitions:The desire for territorial expansion fueled political ambitions. Manifest Destiny, the belief in the United States’ divinely ordained mission to expand westward, became a rallying cry for expansionists.
- Social Factors:A spirit of adventure and the desire to escape societal constraints motivated many to venture into the unknown frontiers.
Major Events of Westward Expansion
The westward expansion unfolded through a series of significant events:
- Louisiana Purchase (1803):The United States doubled its size with the purchase of the Louisiana Territory from France.
- Lewis and Clark Expedition (1804-1806):This expedition explored the Louisiana Purchase and opened up the vast Northwest.
- Trail of Tears (1830s):The forced removal of Native American tribes from their ancestral lands to make way for white settlers.
- Mexican-American War (1846-1848):The war resulted in the United States acquiring the present-day states of California, Nevada, Utah, and parts of Arizona, New Mexico, and Colorado.
- California Gold Rush (1848-1855):The discovery of gold in California triggered a massive influx of settlers and further accelerated westward expansion.
- Transcontinental Railroad (1869):The completion of the railroad connected the East and West Coasts, transforming transportation and trade.
Impact of Westward Expansion
Westward expansion had a profound impact on the United States:
- Territorial Expansion:The United States expanded its territory from coast to coast, becoming one of the largest nations in the world.
- Economic Growth:The acquisition of new lands and resources fueled economic growth and prosperity.
- Cultural Diversity:Westward expansion brought together people from diverse backgrounds, shaping the nation’s cultural landscape.
- Environmental Transformation:The expansion led to the displacement of Native American tribes and the exploitation of natural resources, resulting in significant environmental changes.
- National Identity:Westward expansion fostered a sense of national identity and destiny, shaping the United States’ self-perception as a nation on a mission.
The Civil War
The Civil War, fought from 1861 to 1865, was a defining moment in American history. Its causes were complex and multifaceted, rooted in the nation’s political, economic, and social fabric.
Causes of the Civil War
- Sectionalism:Deep-seated differences between the Northern and Southern states over economic, political, and social issues, including slavery, tariffs, and states’ rights.
- Slavery:The institution of slavery, particularly its expansion into new territories, became a major point of contention between the North and South.
- Political Polarization:The rise of the Republican Party, which opposed the expansion of slavery, and the increasing sectionalism led to political gridlock and heightened tensions.
Timeline of Major Events
- 1861:Confederate forces attack Fort Sumter, South Carolina, sparking the start of the war.
- 1863:Battle of Gettysburg, a pivotal Union victory that turned the tide of the war.
- 1865:Confederate General Robert E. Lee surrenders to Union General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Court House, effectively ending the war.
Impact of the Civil War
- End of Slavery:The war resulted in the abolition of slavery through the ratification of the 13th Amendment.
- Reconstruction:A period of rebuilding and reintegrating the former Confederate states into the Union.
- National Unity:Despite the devastation and loss of life, the war ultimately strengthened the bonds of the United States as a unified nation.
Reconstruction
Reconstruction was the period in American history that followed the Civil War. It began in 1865 and lasted until 1877. The goals of Reconstruction were to reunite the country, rebuild the South, and protect the rights of African Americans.The major events of Reconstruction included the passage of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments to the Constitution, which abolished slavery, granted citizenship to African Americans, and gave them the right to vote.
The Reconstruction Acts of 1867 and 1868 divided the South into military districts and placed it under the control of the federal government. The Ku Klux Klan, a white supremacist organization, terrorized African Americans and prevented them from exercising their rights.Reconstruction
had a significant impact on the United States. It helped to reunite the country and rebuild the South. It also led to the passage of laws that protected the rights of African Americans. However, Reconstruction was also a time of great violence and turmoil.
The Ku Klux Klan and other white supremacist groups terrorized African Americans and prevented them from exercising their rights. Reconstruction ended in 1877 with the withdrawal of federal troops from the South.
Goals of Reconstruction
The goals of Reconstruction were to:* Reunite the country
- Rebuild the South
- Protect the rights of African Americans
Major Events of Reconstruction
The major events of Reconstruction included:* The passage of the 13th, 14th, and 15th Amendments to the Constitution
- The Reconstruction Acts of 1867 and 1868
- The Ku Klux Klan terrorized African Americans
Impact of Reconstruction
Reconstruction had a significant impact on the United States. It helped to:* Reunite the country
- Rebuild the South
- Protect the rights of African Americans
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution marked a significant turning point in human history, bringing about unprecedented technological advancements and profound societal changes. This transformation, which originated in Great Britain in the late 18th century, gradually spread to other parts of the world, including the United States.
The Industrial Revolution was driven by a combination of factors, including:
- Agricultural Revolution:Innovations in farming techniques, such as crop rotation and the use of fertilizers, led to increased agricultural productivity, freeing up labor for industrial pursuits.
- Population Growth:A surge in population provided a ready labor force for factories and contributed to increased demand for goods.
- Technological Advancements:Inventions such as the steam engine, the cotton gin, and the power loom revolutionized production processes and increased efficiency.
- Availability of Raw Materials:The United States possessed vast natural resources, such as coal, iron ore, and timber, which fueled industrial growth.
- Capital Investment:The accumulation of wealth from agriculture and commerce provided capital for investment in industrial ventures.
Timeline of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution unfolded gradually over several decades:
- 1760s:James Watt invents the steam engine, a major power source for factories.
- 1793:Eli Whitney invents the cotton gin, revolutionizing cotton production in the United States.
- 1800s:Steam-powered ships and railroads emerge, facilitating transportation of goods and people.
- 1830s:The telegraph is invented, enabling faster communication.
- 1870s:The Bessemer process revolutionizes steel production, making it stronger and cheaper.
Impact of the Industrial Revolution on the United States
The Industrial Revolution had a profound impact on the United States, leading to:
- Economic Growth:Industrialization boosted productivity and created new industries, leading to economic prosperity.
- Urbanization:Factories attracted workers to cities, resulting in rapid urban growth.
- Transportation Revolution:Steam-powered ships and railroads connected different regions of the country, facilitating trade and travel.
- Social Changes:Industrialization led to the emergence of a working class and the development of labor unions.
- Environmental Impact:Industrial processes polluted the environment, leading to air and water pollution.
The Progressive Era
The Progressive Era was a period of social and political reform in the United States that began in the late 19th century and lasted until the early 20th century. The movement was characterized by a belief in the power of government to improve society and a commitment to social justice.
Goals of the Progressive Era
- To promote social justice and equality.
- To improve the lives of the working class.
- To regulate big business and protect consumers.
- To increase the power of government to solve social problems.
Major Events of the Progressive Era
- The passage of the Sherman Antitrust Act (1890) and the Clayton Antitrust Act (1914) to break up monopolies.
- The establishment of the Federal Reserve System (1913) to regulate the banking industry.
- The passage of the Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) and the Meat Inspection Act (1906) to protect consumers from unsafe products.
- The passage of the 16th Amendment (1913) to allow for the creation of a federal income tax.
- The passage of the 17th Amendment (1913) to allow for the direct election of senators.
Impact of the Progressive Era
The Progressive Era had a profound impact on the United States. The movement led to a number of important reforms that improved the lives of millions of Americans. It also helped to lay the foundation for the modern American welfare state.
World War I
World War I, also known as the Great War, was a global conflict that took place from 1914 to 1918, primarily in Europe. The war involved all the great powers of the time, including Russia, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, and the United States, and spanned a global scale.
The main causes of the war were a complex interplay of factors, including militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism.
Causes of World War I
Militarism:The European powers had been engaged in an arms race in the years leading up to the war, with each country building up its military strength. This created a sense of insecurity and fear among the powers, as each feared being attacked by the others.
Alliances:By 1914, Europe was divided into two main alliances: the Triple Alliance (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy) and the Triple Entente (France, Russia, and the United Kingdom). These alliances created a situation where any conflict between two countries could quickly escalate into a wider war.
Imperialism:The European powers were all competing for colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Middle East. This competition for resources and territory created tensions between the powers and contributed to the outbreak of war. Nationalism:The rise of nationalism in Europe led to a sense of pride and patriotism in each country.
This nationalism made it difficult for the powers to compromise and resolve their differences peacefully.
Timeline of Major Events of World War I
1914
June 28
Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria is assassinated in Sarajevo, Bosnia.
July 28
Austria-Hungary declares war on Serbia.
August 1
Germany declares war on Russia.
August 3
Germany declares war on France.
August 4
United Kingdom declares war on Germany. 1915
February
Battle of Gallipoli begins.
May
Italy joins the Allies.
September
Bulgaria joins the Central Powers. 1916
February
Battle of Verdun begins.
July
Battle of the Somme begins. 1917
February
United States declares war on Germany.
March
Russian Revolution begins.
November
Bolsheviks seize power in Russia. 1918
March
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk is signed between Russia and Germany.
June
Second Battle of the Marne begins.
November 11
Armistice is signed between the Allies and Germany, ending the war.
Impact of World War I on the United States
The United States entered World War I in 1917, after Germany resumed unrestricted submarine warfare in the Atlantic Ocean. The United States’ entry into the war helped to turn the tide against Germany and led to the Allied victory. However, the war also had a significant impact on the United States, both economically and socially.
Economically,the war led to a boom in American industry. The United States supplied the Allies with food, weapons, and other materials, which helped to fuel the American economy. The war also led to the development of new industries, such as the aircraft industry.
Socially,the war had a profound impact on the United States. The war led to the deaths of over 100,000 American soldiers, and it also caused widespread social unrest. The war also led to the rise of new social movements, such as the women’s suffrage movement.
The Roaring Twenties
The Roaring Twenties, a period of economic prosperity and social change in the United States following World War I, witnessed significant transformations that left a lasting impact on the nation.
Social Changes
- Urbanization and Mass Culture:Cities boomed as people migrated from rural areas, fostering the growth of mass culture, including movies, radio, and sports.
- Women’s Rights and Flappers:Women gained more social and political freedoms, challenging traditional gender roles. The “flappers” symbolized this cultural shift.
- Prohibition and Crime:The prohibition of alcohol led to a rise in organized crime and bootlegging, which further weakened public trust in the government.
Economic Changes
- Consumerism and Technology:Mass production and advertising fueled consumerism, creating new industries and transforming the economy.
- Stock Market Boom:Speculation and easy credit led to a stock market boom, culminating in the infamous 1929 crash.
- Agriculture Crisis:Farmers faced economic hardship due to overproduction and falling prices, contributing to the Great Depression.
Major Events
- Teapot Dome Scandal:A government corruption scandal involving oil reserves damaged public confidence.
- Sacco and Vanzetti Trial:The trial and execution of two Italian immigrants for murder raised concerns about social injustice.
- The Great Mississippi Flood:A devastating flood in 1927 displaced thousands and caused widespread damage.
Impact on the United States
The Roaring Twenties left a profound impact on the United States:
- Cultural Shift:It ushered in a new era of social and cultural freedom, challenging traditional values.
- Economic Instability:The stock market crash and subsequent Great Depression highlighted the fragility of the economy.
- Political Polarization:Social and economic issues divided the nation, laying the groundwork for future political conflicts.
The Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression that began in the United States in the 1930s. The global gross domestic product (GDP) decreased by an estimated 15% between 1929 and 1932.
The causes of the Great Depression are complex and still debated by economists, but some of the key factors include:
- Overproduction of goods and services, leading to a decline in prices and profits.
- A collapse in the stock market, which led to a loss of confidence in the financial system.
- A reduction in consumer spending, as people lost their jobs and incomes.
- The Smoot-Hawley Tariff, which raised tariffs on imported goods and led to a decline in international trade.
The Great Depression had a devastating impact on the United States. Unemployment reached 25%, and millions of people lost their homes and savings. The economy did not fully recover until the outbreak of World War II in 1939.
Timeline of the Great Depression
- 1929:The stock market crashes, marking the beginning of the Great Depression.
- 1930:Unemployment reaches 8.7%, and the Smoot-Hawley Tariff is passed.
- 1931:The Gross National Product (GNP) falls by 8.5%, and the banking crisis worsens.
- 1932:Unemployment reaches 25%, and the Reconstruction Finance Corporation is created to help banks and businesses.
- 1933:Franklin D. Roosevelt is elected president and launches the New Deal, a series of programs designed to help the economy recover.
- 1939:The outbreak of World War II helps to end the Great Depression.
World War II
World War II, also known as the Second World War, was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world’s countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers.
The causes of World War II are complex, but some of the most important factors include the rise of fascism and militarism in Europe, the failure of the League of Nations, and the economic depression of the 1930s.
Timeline of Major Events
- 1939: Germany invades Poland, starting World War II.
- 1940: Germany conquers Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France.
- 1941: Germany invades the Soviet Union.
- 1941: Japan attacks Pearl Harbor, bringing the United States into the war.
- 1942: Japan conquers much of Southeast Asia.
- 1943: The Allies begin to turn the tide of the war with victories in North Africa and the Pacific.
- 1944: The Allies liberate France and Italy.
- 1945: The Allies defeat Germany and Japan, ending World War II.
Impact of World War II on the United States
World War II had a profound impact on the United States. The war led to the deaths of over 400,000 Americans and the mobilization of the entire economy. It also led to the creation of the United Nations and the beginning of the Cold War.
The Cold War
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies that lasted from the mid-1940s to the early 1990s. It was characterized by an arms race, propaganda campaigns, economic competition, and proxy wars, but never escalated into a full-scale nuclear war.
Origins
- Ideological differences between capitalism and communism
- Soviet expansionism in Eastern Europe after World War II
- US desire to contain the spread of communism
Major Events
- Berlin Blockade (1948-1949)
- Korean War (1950-1953)
- Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)
- Vietnam War (1954-1975)
- Fall of the Berlin Wall (1989)
Impact on the United States
- Increased military spending and development of new weapons
- Expansion of the national security state
- Rise of the military-industrial complex
- Domestic political polarization and McCarthyism
- Global superpower status
The Civil Rights Movement
The Civil Rights Movement in the United States was a period of social activism and protest that aimed to end racial discrimination and segregation. The movement’s roots can be traced back to the abolitionist movement of the 19th century, but it gained momentum in the mid-20th century.The
Civil Rights Movement was sparked by a number of factors, including:
- The legacy of slavery and segregation
- The rise of the Black Power movement
- The growing awareness of the injustices faced by African Americans
- The leadership of Martin Luther King Jr. and other civil rights activists
Timeline of Major Events
The Civil Rights Movement was marked by a number of key events, including:
- 1954: Brown v. Board of Education
- 1955: Montgomery Bus Boycott
- 1963: March on Washington
- 1964: Civil Rights Act
- 1965: Voting Rights Act
Impact of the Civil Rights Movement
The Civil Rights Movement had a profound impact on the United States. It led to the passage of landmark legislation that outlawed discrimination and segregation. It also helped to raise awareness of the injustices faced by African Americans and other minorities.
The Civil Rights Movement continues to inspire activists and leaders today.
The Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a complex and protracted conflict that lasted from the early 1950s to 1975. It was a major turning point in American history, and its legacy continues to be debated today.
Causes of the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War had its roots in the Cold War and the global struggle between communism and capitalism. After World War II, Vietnam was divided into two countries: North Vietnam, which was communist, and South Vietnam, which was anti-communist. The United States supported South Vietnam, while the Soviet Union supported North Vietnam.
The conflict in Vietnam escalated in the early 1960s, as the United States became increasingly involved in the war. In 1965, the United States began bombing North Vietnam, and in 1967, it sent ground troops to South Vietnam.
Timeline of the Vietnam War
- 1954: The Geneva Accords divide Vietnam into two countries: North Vietnam and South Vietnam.
- 1964: The Gulf of Tonkin incident leads to the United States bombing North Vietnam.
- 1965: The United States sends ground troops to South Vietnam.
- 1968: The Tet Offensive is a major turning point in the war.
- 1973: The Paris Peace Accords are signed, ending the war.
- 1975: North Vietnam invades South Vietnam, and the war ends with the fall of Saigon.
Impact of the Vietnam War on the United States
The Vietnam War had a profound impact on the United States. The war was unpopular with the American public, and it led to widespread protests and demonstrations. The war also resulted in the deaths of more than 58,000 American soldiers.
The Vietnam War also had a significant impact on American politics. The war led to the rise of the anti-war movement, and it contributed to the decline of public trust in the government.
The Watergate Scandal
The Watergate Scandal was a major political scandal that occurred in the United States during the 1970s. It involved the break-in of the Democratic National Committee (DNC) headquarters at the Watergate office complex in Washington, D.C., and the subsequent cover-up of the incident by the Nixon administration.
Events of the Watergate Scandal
- On June 17, 1972, five men were arrested for breaking into the DNC headquarters. They were carrying wiretapping equipment and other materials.
- The investigation into the break-in quickly led to the Nixon administration. It was revealed that the White House had been involved in the planning and execution of the break-in.
- President Nixon tried to cover up the scandal, but he was eventually forced to resign on August 9, 1974.
Impact of the Watergate Scandal
The Watergate Scandal had a profound impact on the United States. It led to a loss of confidence in the government and a decline in the popularity of the Republican Party.
- The scandal also led to the passage of new laws to strengthen the independence of the judiciary and to prevent future abuses of power by the executive branch.
Lessons Learned from the Watergate Scandal
The Watergate Scandal taught us several important lessons:
- The importance of a free and independent press.
- The importance of checks and balances in government.
- The importance of accountability and transparency in government.
The Reagan Revolution
The Reagan Revolution was a period of significant political, economic, and social change in the United States during the 1980s. It was characterized by the policies of President Ronald Reagan, who sought to reduce the size and scope of government, promote economic growth, and strengthen the military.
paragraphThe goals of the Reagan Revolution were to reduce government spending, cut taxes, deregulate the economy, and increase defense spending. The major events of the Reagan Revolution included the passage of the Economic Recovery Tax Act of 1981, the deregulation of the airline, trucking, and telecommunications industries, and the increase in military spending.
Impact of the Reagan Revolution
The Reagan Revolution had a significant impact on the United States. It led to a reduction in the size and scope of government, an increase in economic growth, and a strengthening of the military. However, it also led to an increase in the national debt and a widening of the gap between rich and poor.
The End of the Cold War: Period 7 Apush Study Guide

The Cold War, a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, officially ended in 1991. Several factors contributed to its conclusion, including the rise of Mikhail Gorbachev in the Soviet Union and his policies of glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring), as well as the growing economic and political challenges faced by the Soviet Union.
Impact on the United States
The end of the Cold War had a profound impact on the United States. The United States emerged as the sole superpower, with no major rival to challenge its global influence. This allowed the United States to focus more on domestic issues and to reduce its military spending.
The end of the Cold War also led to a period of economic growth and prosperity in the United States.
Challenges Facing the United States
Despite the positive impacts of the end of the Cold War, the United States also faced a number of challenges. These challenges included:
- The rise of new global powers, such as China and India.
- The spread of terrorism and nuclear proliferation.
- The growing gap between rich and poor.
- The environmental crisis.
The United States continues to face these challenges today. However, the end of the Cold War has given the United States the opportunity to focus on these challenges and to work towards a more prosperous and peaceful future.
The Clinton Era
The Clinton Era, marked by the presidency of Bill Clinton from 1993 to 2001, was a period of economic prosperity and relative peace. The era saw the enactment of significant legislation, including the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act (PRWORA).
Domestic Policy, Period 7 apush study guide
During the Clinton Era, the United States experienced a period of economic expansion. The unemployment rate fell to its lowest level in decades, and the stock market reached record highs. Clinton also signed into law the Family and Medical Leave Act, which provided workers with unpaid leave for family or medical reasons.
Foreign Policy
In foreign policy, Clinton focused on expanding trade and promoting democracy. He negotiated the Dayton Accords, which ended the Bosnian War, and he intervened in Kosovo to prevent ethnic cleansing. Clinton also ordered airstrikes against Iraq in response to its refusal to comply with UN weapons inspections.
Challenges
Despite the economic prosperity and foreign policy successes, the Clinton Era was also marked by challenges. The Whitewater scandal, a real estate investment controversy, led to Clinton’s impeachment by the House of Representatives. However, he was acquitted by the Senate.
Clinton also faced criticism for his handling of the Rwanda genocide and the Monica Lewinsky scandal.
The Bush Era
The Bush Era refers to the presidency of George W. Bush, who served as the 43rd President of the United States from 2001 to 2009. This era was marked by significant events, both domestically and internationally, including the September 11 attacks, the subsequent War on Terror, and the Great Recession.
The War on Terror
Following the September 11 attacks, the Bush administration launched the War on Terror, a global campaign against terrorism. This campaign included the invasion of Afghanistan in 2001 and the invasion of Iraq in 2003.
The Great Recession
The Great Recession, which began in December 2007, was the most severe economic downturn since the Great Depression. The recession led to widespread job losses, foreclosures, and a decline in the stock market.
Challenges Facing the United States
The Bush Era was marked by a number of challenges facing the United States, including:
- The ongoing War on Terror
- The Great Recession
- The rising cost of healthcare
- The growing national debt
- Climate change
The Obama Era
The Obama Era refers to the presidency of Barack Obama, the 44th President of the United States, from 2009 to 2017. Obama’s presidency was marked by significant events and changes in the United States.
One of the major events of the Obama Era was the passage of the Affordable Care Act, also known as Obamacare, in 2010. This healthcare reform law expanded health insurance coverage to millions of Americans who previously lacked it.
Another major event was the end of the Iraq War in 2011 and the drawdown of troops in Afghanistan. Obama also authorized the raid that killed Osama bin Laden, the leader of al-Qaeda, in 2011.
The Obama Era also saw the rise of social media and the increasing use of technology in daily life. The economy also recovered from the Great Recession, although income inequality continued to be a challenge.
Overall, the Obama Era was a period of significant change and progress for the United States. Obama’s presidency was marked by both successes and challenges, but he left office with high approval ratings.
The Trump Era
The Trump Era refers to the presidency of Donald Trump, which spanned from 2017 to 2021. It was a period marked by significant political, social, and economic changes in the United States.The Trump Era witnessed several major events, including the implementation of tax cuts, the withdrawal of the United States from the Trans-Pacific Partnership and the Paris Agreement, the appointment of conservative judges to the Supreme Court, and the impeachment of Trump by the House of Representatives.
Impact on the United States
The Trump Era had a profound impact on the United States. The tax cuts led to increased economic growth, but also contributed to a widening of the budget deficit. The withdrawal from international agreements strained relationships with allies and raised concerns about the United States’ commitment to global leadership.
The appointment of conservative judges to the Supreme Court shifted the balance of power within the judicial branch and is likely to have long-term implications for American law. The impeachment of Trump deepened political divisions and raised questions about the future of American democracy.
Challenges Facing the United States
The Trump Era also presented a number of challenges to the United States. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has had a devastating impact on the economy and public health. The rise of political polarization has made it difficult to address important issues facing the country, such as climate change and gun violence.
The Trump Era also saw an increase in racial tensions and a decline in trust in institutions. These challenges will continue to shape the United States in the years to come.
The Biden Era
The Biden Era began on January 20, 2021, with the inauguration of Joe Biden as the 46th President of the United States. The era has been marked by a number of significant events, including the COVID-19 pandemic, the withdrawal of US troops from Afghanistan, and the passage of the American Rescue Plan Act.
Domestic Policy, Period 7 apush study guide
One of the most significant events of the Biden Era has been the COVID-19 pandemic. The pandemic has had a devastating impact on the United States, causing widespread illness and death, as well as economic hardship. The Biden administration has taken a number of steps to address the pandemic, including providing financial assistance to individuals and businesses, and investing in the development and distribution of vaccines.Another
major event of the Biden Era has been the withdrawal of US troops from Afghanistan. The withdrawal was completed in August 2021, after 20 years of war. The withdrawal was controversial, and has been criticized by some for being too hasty and for leaving Afghanistan vulnerable to the Taliban.The
Biden administration has also passed a number of significant pieces of legislation, including the American Rescue Plan Act. The American Rescue Plan Act is a $1.9 trillion economic stimulus package that was designed to help the United States recover from the COVID-19 pandemic.
The act includes provisions for direct payments to individuals, expanded unemployment benefits, and funding for state and local governments.
Foreign Policy
In foreign policy, the Biden administration has focused on repairing relationships with US allies that were damaged during the Trump administration. The Biden administration has also taken a more aggressive approach to China, which it sees as a major strategic competitor.The
Biden administration has also been involved in a number of international negotiations, including the ongoing talks with Iran over its nuclear program. The Biden administration has also been working to address the humanitarian crisis in Yemen, and has called for an end to the war in that country.
Challenges
The Biden Era has been marked by a number of challenges, including the COVID-19 pandemic, the withdrawal of US troops from Afghanistan, and the ongoing economic crisis. The Biden administration has also faced criticism for its handling of the border crisis and the rise in inflation.Despite
the challenges, the Biden administration has made progress on a number of important issues. The administration has passed a number of significant pieces of legislation, including the American Rescue Plan Act, and has taken steps to address the COVID-19 pandemic.
The administration has also made progress in repairing relationships with US allies and has taken a more aggressive approach to China.The Biden Era is still in its early stages, and it is too early to say what the long-term impact of the era will be.
However, the era has already been marked by a number of significant events, and it is clear that the Biden administration is facing a number of challenges.
Essential FAQs
What are the key principles of the Constitution?
The Constitution establishes the principles of popular sovereignty, limited government, separation of powers, checks and balances, and individual rights.
What were the major events of the Civil War?
The major events of the Civil War include the Battle of Fort Sumter, the Battle of Gettysburg, the Battle of Vicksburg, and the surrender of General Robert E. Lee at Appomattox Court House.
What were the causes of the Great Depression?
The causes of the Great Depression include the stock market crash of 1929, the collapse of the banking system, and the decline in international trade.