Truss locations are noted on the, serving as crucial indicators of the structural integrity and stability of a building or bridge. Understanding their purpose, placement, and analysis is paramount for ensuring the safety and longevity of these structures.
Trusses, intricate frameworks of connected members, play a vital role in distributing loads and resisting forces within a structure. Their placement is meticulously determined based on factors such as the span of the structure, the weight it must bear, and the architectural design.
Truss Locations
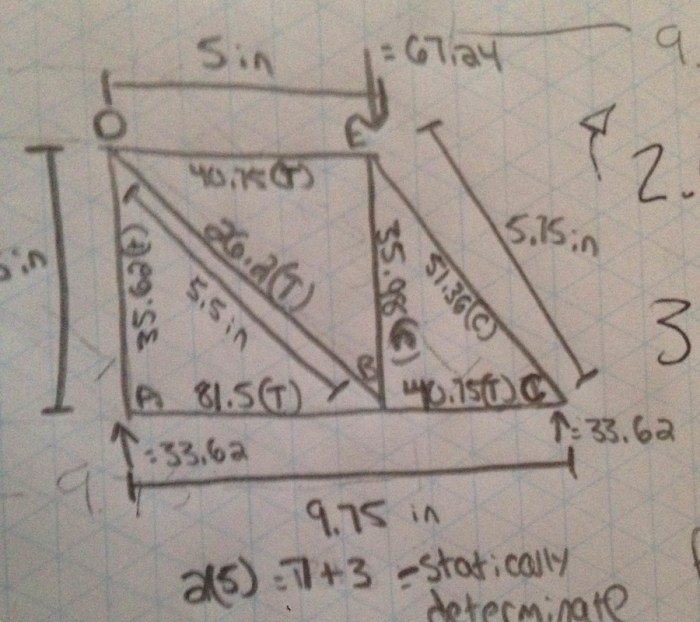
Truss locations are carefully determined based on several factors, including the structural requirements of the building, the span of the roof, and the availability of support points. Trusses are typically placed at regular intervals along the length of the building, with the distance between trusses depending on the size and weight of the roof.
In some cases, trusses may be placed at varying intervals to accommodate specific architectural features or to provide additional support for heavier roof loads.
Purpose of Truss Locations
- To transfer the weight of the roof to the supporting walls or columns.
- To provide structural stability to the roof.
- To create a framework for attaching the roof sheathing and other roofing materials.
- To allow for the installation of insulation, ventilation, and other building systems within the roof cavity.
Truss Design
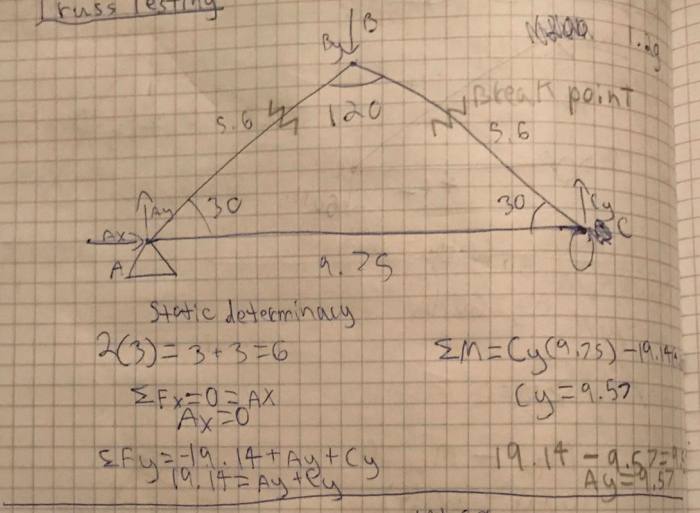
The design of trusses is based on the principles of structural mechanics, which involves the analysis of forces and moments acting on the truss members. The design process typically involves the following steps:
Types of Trusses
- Truss Type:Trusses come in various types, each with its own unique design and characteristics. Common truss types include Pratt trusses, Howe trusses, and Warren trusses.
- Material Selection:Trusses can be constructed from a variety of materials, including wood, steel, and aluminum. The choice of material depends on factors such as the size, weight, and cost of the truss.
- Structural Analysis:Structural analysis is performed to determine the forces and moments acting on the truss members. This analysis helps to ensure that the truss is designed to withstand the applied loads.
- Design Optimization:The truss design is optimized to minimize the weight and cost while ensuring that the truss meets the structural requirements.
Truss Analysis
Truss analysis is an essential step in the design process, as it allows engineers to assess the stability and strength of the truss. The analysis typically involves the following steps:
Methods of Truss Analysis
- Graphical Methods:Graphical methods, such as the method of sections and the method of joints, can be used to analyze simple trusses.
- Analytical Methods:Analytical methods, such as the matrix stiffness method and the finite element method, can be used to analyze complex trusses.
- Software Analysis:Computer software can be used to perform truss analysis quickly and efficiently.
Truss Connections

Truss connections are critical to the structural integrity of the truss. The type of connection used depends on the materials used in the truss and the loads that the truss will be subjected to.
Types of Truss Connections
- Bolted Connections:Bolted connections are commonly used in steel trusses. Bolts are inserted through holes in the truss members and tightened to create a secure connection.
- Welded Connections:Welded connections are used to join steel truss members permanently. Welding creates a strong and rigid connection between the members.
- Nailed Connections:Nailed connections are used in wood trusses. Nails are driven through the truss members to create a secure connection.
- Pinned Connections:Pinned connections allow for rotation between the truss members. Pinned connections are typically used at the supports of the truss.
Truss Inspection and Maintenance

Regular inspection and maintenance are essential to ensure the long-term integrity of trusses. Inspections should be performed by a qualified inspector who can identify any signs of damage or deterioration.
Truss Inspection Procedures, Truss locations are noted on the
- Visual Inspection:A visual inspection of the truss should be performed to identify any visible signs of damage, such as cracks, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Load Testing:Load testing can be performed to assess the strength and stability of the truss. Load testing involves applying a known load to the truss and measuring the truss’s response.
- Non-Destructive Testing:Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing and radiography, can be used to detect hidden damage within the truss members.
Truss Rehabilitation and Repair
Damaged trusses can be repaired or rehabilitated to restore their structural integrity. The type of repair or rehabilitation required will depend on the extent of the damage.
Truss Repair Methods
- Splicing:Splicing involves cutting out the damaged section of the truss member and replacing it with a new section.
- Reinforcement:Reinforcement involves adding additional material to the truss member to increase its strength.
- Replacement:In some cases, it may be necessary to replace the entire truss member.
Query Resolution: Truss Locations Are Noted On The
What factors determine the placement of trusses?
The placement of trusses is influenced by the span of the structure, the weight it must bear, and the architectural design.
What is the purpose of truss analysis?
Truss analysis involves calculating the forces acting on each truss member to assess the stability and strength of the trusses.
Why are proper truss connections important?
Proper truss connections ensure that the trusses can effectively transfer loads and resist forces, maintaining the structural integrity of the building or bridge.