Elite democracy pros and cons – In the realm of governance, elite democracy stands as a unique and intriguing model, sparking debates about its merits and drawbacks. Join us as we delve into the intricacies of elite democracy, examining its potential benefits and limitations.
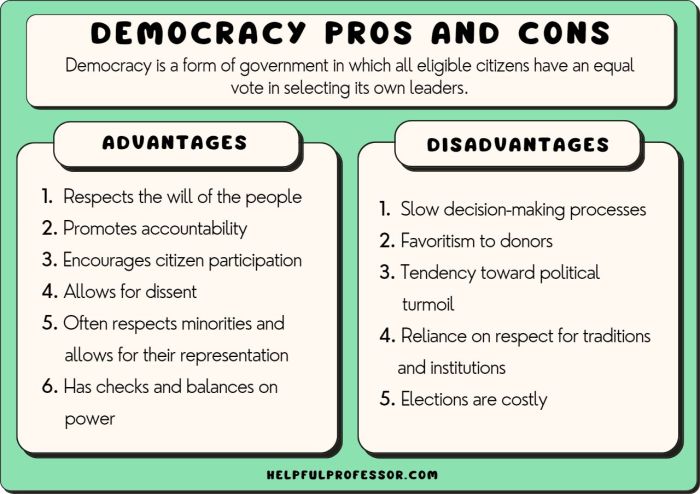
Elite democracy, a system where power is vested in a select group of qualified individuals, offers a compelling proposition. Advocates argue for its ability to foster political stability, enhance decision-making, and safeguard minority interests. Yet, critics raise concerns about the potential for elitism, suppression of dissent, and limited representation.
Pros of Elite Democracy
Elite democracy, a system where power is concentrated in the hands of a select group of qualified individuals, offers several advantages.
Increased Political Stability and Reduced Corruption, Elite democracy pros and cons
Elite democracies tend to experience greater political stability due to the expertise and experience of their leaders. These leaders are often well-educated and have a deep understanding of governance, allowing them to make informed decisions and maintain order within the society.
Additionally, elite democracies often have strong anti-corruption measures in place, reducing the likelihood of corrupt practices and ensuring the integrity of the political system.
Cons of Elite Democracy

While elite democracy offers advantages, it also presents certain drawbacks that warrant consideration.
Potential for Oligarchy and Suppression of Dissent
Elite democracies can be susceptible to oligarchy, where a small, wealthy, and influential elite exerts excessive power over decision-making. This can lead to the suppression of dissent and the silencing of marginalized voices. The elite may have vested interests that conflict with the broader public interest, resulting in policies that favor the privileged few at the expense of the majority.
Limited Representation of the General Population
In elite democracies, the general population may have limited representation in the decision-making process. The elite may not fully understand or prioritize the needs and concerns of ordinary citizens, leading to policies that do not adequately address their interests. This lack of representation can result in a sense of alienation and disenfranchisement among the general population.
Lack of Accountability and Transparency in Decision-Making
Elite democracies may lack sufficient accountability and transparency in decision-making. The elite may operate behind closed doors, making decisions without consulting or informing the public. This lack of transparency can undermine trust in the government and make it difficult for citizens to hold their leaders accountable.
Historical Examples of Elite Democracy
Throughout history, there have been numerous examples of elite democracies, where power was concentrated in the hands of a small, privileged group.
The Roman Republic
The Roman Republic, established in 509 BC, is a prime example of an elite democracy. Power was vested in the hands of the patricians, a wealthy and aristocratic class, who controlled the Senate and held most political offices. While the Roman Republic had democratic elements, such as popular assemblies where citizens could vote, these assemblies were largely dominated by the patricians.
Elite democracy has its pros and cons, but it’s essential to consider the bigger picture. Just like how AJ Loyal Income Tax Service helps individuals navigate complex tax codes, understanding the nuances of elite democracy is crucial. It empowers citizens to make informed decisions that shape the future of their society, ensuring that the system serves the needs of all, not just the privileged few.
The Venetian Republic
The Venetian Republic, founded in the 7th century AD, was another notable example of an elite democracy. Power was concentrated in the hands of a small group of wealthy merchant families, who formed the Great Council. The Great Council elected the Doge, the head of state, and made all important decisions.
The United States during the Founding Era
The United States during the Founding Era (late 18th century) also exhibited characteristics of an elite democracy. While the Declaration of Independence proclaimed that all men are created equal, political power was largely concentrated in the hands of a small group of wealthy landowners and merchants.
These elites dominated the Constitutional Convention and shaped the early American political system.
Modern Applications of Elite Democracy

Elite democracy continues to be applied in modern contexts, often in the form of technocratic governments, meritocratic systems, and corporate boards.
Technocratic governments are led by experts with specialized knowledge in relevant fields, while meritocratic systems emphasize the selection of leaders based on their abilities and qualifications. Corporate boards, responsible for overseeing the management of companies, often consist of individuals with extensive experience and expertise in business and finance.
Technocratic Governments
Technocratic governments are led by individuals with specialized knowledge and expertise in relevant fields, such as science, technology, engineering, or economics.
These governments are often formed in times of crisis or instability, when there is a need for specialized knowledge and expertise to address complex problems. For example, in 2016, Italy appointed a technocratic government led by Paolo Gentiloni, an economist, to address the country’s economic crisis.
Meritocratic Systems
Meritocratic systems emphasize the selection of leaders based on their abilities and qualifications, rather than their social status or wealth.
These systems are often used in education and employment, where individuals are selected for positions based on their academic achievements or professional experience. For example, many universities use meritocratic systems to select students for admission, and many companies use meritocratic systems to select employees for promotion.
Corporate Boards
Corporate boards are responsible for overseeing the management of companies and ensuring that they are operating in the best interests of shareholders.
Corporate boards often consist of individuals with extensive experience and expertise in business and finance. These individuals are selected based on their qualifications and ability to contribute to the company’s success. For example, the board of directors of Apple Inc.
includes individuals with experience in technology, finance, and marketing.
Comparison of Elite Democracy to Other Forms of Government: Elite Democracy Pros And Cons

Elite democracy stands out from other forms of government due to its unique characteristics and approaches to governance. Here’s a comparison of elite democracy with other prominent forms of government:
Direct Democracy
Direct democracy involves the direct participation of citizens in decision-making processes. In contrast, elite democracy delegates decision-making authority to a select group of elites.
- Pros:Direct democracy ensures that the will of the people is directly reflected in government decisions.
- Cons:It can be impractical for large and complex societies, as it requires extensive citizen participation and can lead to hasty decisions.
Representative Democracy
Representative democracy employs elected officials to represent the interests of citizens. Elite democracy also utilizes representatives, but the selection process and the power dynamics differ.
- Pros:Representative democracy allows for specialized expertise and deliberation among elected officials.
- Cons:It can be susceptible to corruption and the influence of powerful elites, potentially undermining the responsiveness to citizen concerns.
Authoritarian Regimes
Authoritarian regimes concentrate power in the hands of a single leader or a small group without democratic accountability. Elite democracy, while not fully democratic, still incorporates some elements of citizen participation and accountability.
- Pros:Authoritarian regimes can provide stability and order in times of crisis.
- Cons:They suppress dissent, restrict individual freedoms, and lack transparency and accountability.
The Role of Education in Elite Democracy
In an elite democracy, education plays a pivotal role in ensuring the quality and sustainability of governance. By providing access to quality education for all citizens, promoting critical thinking and civic engagement, and preparing future leaders for the responsibilities of governance, education empowers individuals to actively participate in the decision-making process and hold their leaders accountable.
Ensuring Access to Quality Education for All Citizens
In an elite democracy, access to quality education is not a privilege but a fundamental right. By ensuring that all citizens have equal opportunities to acquire knowledge and skills, regardless of their socioeconomic background, an elite democracy fosters a more informed and engaged citizenry.
- Education empowers individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to understand complex societal issues, analyze information critically, and make informed decisions about their lives and their communities.
- A well-educated populace is more likely to participate in civic activities, engage in political discourse, and hold their leaders accountable for their actions.
Promoting Critical Thinking and Civic Engagement
Education in an elite democracy goes beyond the mere acquisition of knowledge; it also emphasizes the development of critical thinking skills and civic engagement. By encouraging students to question assumptions, evaluate evidence, and form their own opinions, education fosters a citizenry that is capable of making informed decisions and actively participating in the democratic process.
- Critical thinking is essential for evaluating the validity of information, identifying biases, and making sound judgments.
- Civic engagement promotes a sense of responsibility and encourages individuals to participate in their communities, whether through volunteering, advocacy, or political participation.
Preparing Future Leaders for the Responsibilities of Governance
Education plays a crucial role in preparing future leaders for the responsibilities of governance. By providing opportunities for students to develop their leadership skills, learn about public policy, and understand the complexities of governance, education equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively lead and serve their communities.
- Education can provide students with opportunities to develop their leadership skills through extracurricular activities, student government, and community service.
- Courses in public policy, political science, and economics can provide students with the knowledge and understanding necessary to effectively address the challenges facing their communities and the nation.
FAQ
What is the primary benefit of elite democracy?
Elite democracy aims to leverage the expertise and qualifications of a select group to enhance decision-making and governance.
What is a key concern associated with elite democracy?
Critics argue that elite democracy can lead to a concentration of power among a small group, potentially marginalizing the voices of the broader population.