The Sun for One Crossword is a captivating journey that unravels the celestial significance of our radiant star. From its astronomical importance to its profound cultural and mythological depictions, this exploration illuminates the multifaceted nature of the Sun, revealing its profound impact on our planet and our understanding of the universe.
As we delve into the depths of this cosmic subject, we will explore the methods used to study the Sun, uncover the challenges involved in unraveling its mysteries, and marvel at the artistic representations that have captured its essence throughout history.
Crossword Clue Analysis
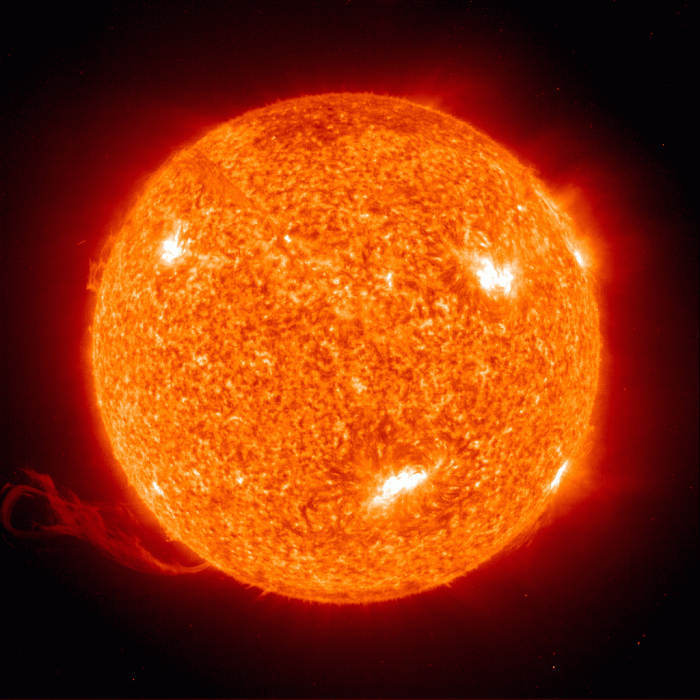
The crossword clue “The sun for one” refers to a celestial body that emits light and heat, serving as the primary energy source for life on Earth.
The answer to this clue is “STAR”, which is a self-luminous celestial body made up of incandescent gas that generates its own energy through nuclear fusion reactions.
Astronomy and the Sun
The Sun is a celestial marvel that plays a central role in our solar system and profoundly impacts life on Earth. It is a massive, incandescent sphere of plasma, radiating colossal amounts of energy and shaping the cosmic landscape.
The Sun’s Astronomical Significance
The Sun is the heart of our solar system, accounting for over 99% of its total mass. It is a G-type main-sequence star, with an age of approximately 4.6 billion years and an expected lifespan of about 10 billion years.
Solving the crossword puzzle for “the sun for one” got me thinking about other words with similar suffixes. I stumbled upon a treasure trove of words with the suffix fy , which brought me back to the crossword and helped me complete it with ease.
The Sun’s immense gravitational pull keeps the planets, moons, asteroids, and comets of our solar system in orbit, maintaining the celestial dance that defines our cosmic neighborhood.
The Sun’s Role in Our Solar System
The Sun’s radiant energy sustains life on Earth and drives various planetary processes. Its ultraviolet radiation helps shape Earth’s atmosphere, protecting it from harmful solar winds.
The Sun’s magnetic field interacts with Earth’s magnetic field, creating the auroras borealis and australis, enchanting celestial displays that paint the skies in vibrant hues.
The Sun’s Effects on Life on Earth
The Sun’s energy is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy, providing the foundation for the food chain and sustaining life on Earth.
The Sun’s warmth regulates Earth’s temperature, making it habitable for a diverse range of organisms. Its daily and seasonal cycles influence biological rhythms, shaping the behavior of plants, animals, and humans alike.
Cultural and Mythological Depictions of the Sun: The Sun For One Crossword

The Sun, as a celestial body, has held a prominent place in human cultures and mythologies worldwide. Different civilizations have attributed unique symbolism and meanings to the Sun, shaping their beliefs, art, and traditions.
Ancient Egypt
- The ancient Egyptians revered the Sun as the god Ra, who represented life, warmth, and light.
- Ra was often depicted as a man with the head of a falcon, adorned with a solar disk.
- The Egyptians built grand temples and monuments dedicated to Ra, including the iconic pyramids of Giza.
Greek Mythology
- In Greek mythology, the Sun was personified as Helios, the god of light and prophecy.
- Helios was often portrayed as a handsome young man driving a golden chariot across the sky.
- The Greeks believed that Helios could see and hear everything, making him a symbol of truth and justice.
Norse Mythology
- The Norse people of Scandinavia worshipped the Sun as Sol, a goddess associated with warmth, fertility, and healing.
- Sol was believed to drive a chariot pulled by two horses named Arvak and Alsvid.
- The Norse myth of Ragnarok, the end of the world, includes the Sun being devoured by the wolf Skoll.
Native American Cultures
- Many Native American tribes held the Sun in high regard as a symbol of life, power, and renewal.
- The Sun Dance, a sacred ceremony practiced by some tribes, was performed to honor the Sun and seek its blessings.
- Native American art often incorporates symbols of the Sun, representing hope, guidance, and protection.
Scientific Study of the Sun
![]()
Studying the Sun, our closest star, is crucial for understanding its impact on Earth’s environment and the solar system. Scientists employ various methods to investigate the Sun’s behavior, composition, and dynamics.
Methods of Solar Study
- Ground-Based Observations:Telescopes on Earth observe the Sun’s surface, atmosphere, and emissions, providing data on sunspots, flares, and other phenomena.
- Space-Based Missions:Satellites and probes, such as NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), collect detailed images and measurements from close proximity to the Sun, studying its magnetic fields, plasma dynamics, and coronal heating.
- Helioseismology:By analyzing the Sun’s oscillations, scientists infer its internal structure, rotation, and magnetic activity.
- Radio Astronomy:Radio telescopes detect emissions from the Sun’s corona and chromosphere, providing insights into its magnetic fields and plasma behavior.
Types of Solar Data
- Surface Images:Photographs capture the Sun’s surface, revealing sunspots, faculae, and other features.
- Spectroscopic Data:Analysis of the Sun’s light reveals its chemical composition, temperature, and velocity.
- Magnetic Field Measurements:Instruments measure the Sun’s magnetic field strength and configuration, which influences its activity.
- Plasma Properties:Probes and satellites measure the density, temperature, and velocity of the Sun’s plasma.
Challenges in Solar Study
Studying the Sun presents unique challenges:
- Extreme Brightness:The Sun’s intense brightness requires specialized instruments and techniques to protect sensitive equipment.
- Variable Activity:The Sun’s activity changes over time, making it difficult to predict and study specific events.
- Distance and Inaccessibility:The Sun’s great distance and the harsh conditions of space limit direct access and in-situ measurements.
Artistic Representations of the Sun
The Sun, a celestial body of immense power and beauty, has captivated artists throughout history, inspiring countless masterpieces across various mediums. From the earliest cave paintings to contemporary sculptures, the Sun’s radiant presence has been captured and interpreted in a myriad of styles and techniques.
Paintings, The sun for one crossword
Artists have long sought to depict the Sun’s ethereal glow and dynamic energy in their paintings. Vincent van Gogh’s vibrant “Sunflowers” series captures the Sun’s warmth and golden hues, while Claude Monet’s “Impression, Sunrise” portrays the Sun’s ephemeral nature as it rises over the horizon.
The Sun’s radiant orb and its surrounding rays have also been a prominent motif in religious iconography, such as the haloes depicted in Byzantine mosaics and Renaissance paintings.
Sculptures
The Sun’s three-dimensional form has been translated into impressive sculptures. The iconic “Colossus of Rhodes,” one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, depicted the Sun god Helios as a towering bronze statue. In modern times, artists like Henry Moore have created abstract sculptures that evoke the Sun’s shape and energy through flowing lines and geometric forms.
Other Art Forms
Beyond paintings and sculptures, the Sun has found expression in various other art forms. Photography has captured the Sun’s dramatic flares and solar eclipses, while cinema has utilized the Sun’s lighting and symbolism to create memorable scenes. In literature, the Sun has served as a potent metaphor for hope, enlightenment, and renewal.
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of the Sun in astronomy?
The Sun is the central star of our solar system, providing light, heat, and energy that sustains life on Earth. It is a hot ball of glowing gases, primarily hydrogen and helium, that emits electromagnetic radiation across the entire spectrum.
How have different cultures depicted the Sun in mythology?
In many cultures, the Sun has been revered as a deity or a symbol of power and life. In ancient Egypt, the Sun god Ra was worshipped as the creator and sustainer of the universe. In Greek mythology, Helios was the personification of the Sun, riding a chariot across the sky each day.
What methods are used to study the Sun?
Scientists use a variety of methods to study the Sun, including telescopes, satellites, and space probes. These tools allow us to observe the Sun’s surface, atmosphere, and magnetic field, and to collect data on its composition, temperature, and activity.